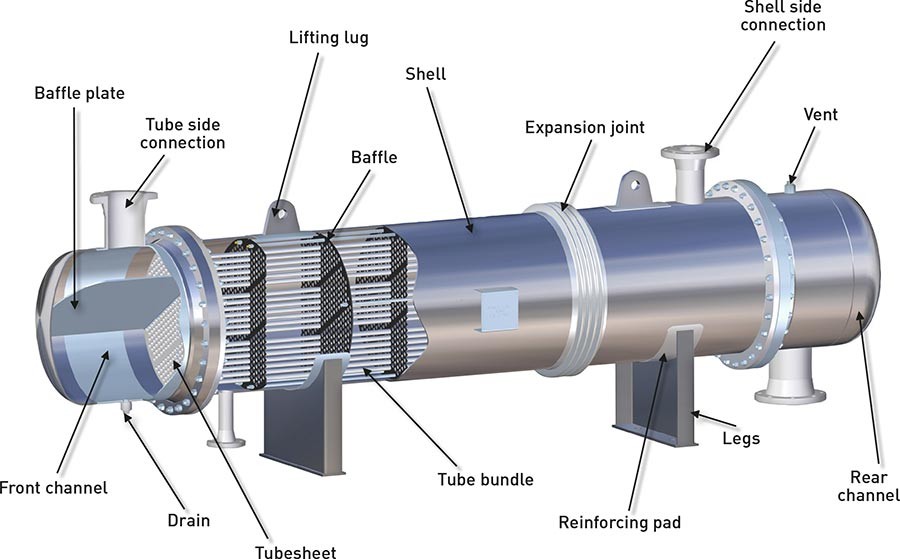
In various industrial and medical contexts, the term “re-tubing” refers to the process of replacing tubes or tubing systems. This procedure is critical for maintaining efficiency, safety, and functionality in a wide range of equipment and devices. Whether it’s in boilers, heat exchanges, medical catheters, or other systems, re-tubing ensures that operations continue smoothly and reliably.
Importance of Re-Tubing
1. Industrial Equipment: In industrial settings, boilers and heat exchanges rely on tubes to transfer heat or fluids efficiently. Over time, these tubes can degrade due to corrosion, wear, or chemical reactions. Re-tubing becomes essential to restore optimal performance and prevent costly downtime.
2. Medical Applications: In the medical field, re-tubing is crucial for maintaining hygiene and patient safety. Catheters and other medical tubes need periodic replacement to minimize the risk of infection and ensure accurate delivery of fluids or medications.
The Re-Tubing Process
1. Assessment and Planning: Before re-tubing, a thorough assessment of the existing tubes is conducted. This includes inspection for wear, corrosion, and any structural damage. Based on this assessment, a plan is developed outlining the scope of work, materials needed, and timeline for completion.
2.Tube Removal: The first step in re-tubing involves removing the old or damaged tubes. This process requires precision to avoid damage to surrounding components and to ensure that the new tubes will fit securely into place.
3. Tube Replacement: New tubes are carefully selected based on material compatibility, size requirements, and operational demands. Installation involves precise fitting and welding or bonding, depending on the application. Quality control measures ensure that the newly installed tubes meet safety and performance standards.
4. Testing and Commissioning: After installation, rigorous testing procedures are carried out to verify the integrity and functionality of the new tubes. This may include pressure testing, fluid flow analysis, and operational trials to ensure that the re-tubed equipment operates efficiently and safely.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Cost and Downtime: Re-tubing can be expensive, especially for large-scale industrial equipment. Downtime during re-tubing procedures may disrupt production schedules, necessitating careful planning and scheduling to minimize economic impact.
2. Material Selection: Choosing the right materials for re-tubing is crucial to ensure compatibility with operational conditions and to extend the lifespan of the equipment. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and fluid composition must be carefully considered.
3. Regulatory Compliance: In medical and certain industrial sectors, re-tubing must adhere to strict regulatory standards to ensure safety and quality. Compliance with regulations ensures that re-tubed equipment meets industry-specific requirements and certifications.
Conclusion
Re-tubing plays a vital role in maintaining the efficiency, safety, and reliability of various equipment and systems across industries. Whether it’s for industrial boilers, medical catheters, or other applications, periodic replacement of tubes ensures that operations continue smoothly and in accordance with safety standards. By understanding the importance of re-tubing and following best practices in the process, industries can enhance operational efficiency and prolong the lifespan of critical equipment.
In summary, re-tubing is not just a maintenance task; it’s a strategic investment in ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of essential machinery and medical devices.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of re-tubing, covering its significance, the process involved, challenges faced, and considerations for various applications. If you have any specific areas you’d like to delve deeper into or need further clarification on, feel free to ask!






